Spark TaskScheduler 源码分析
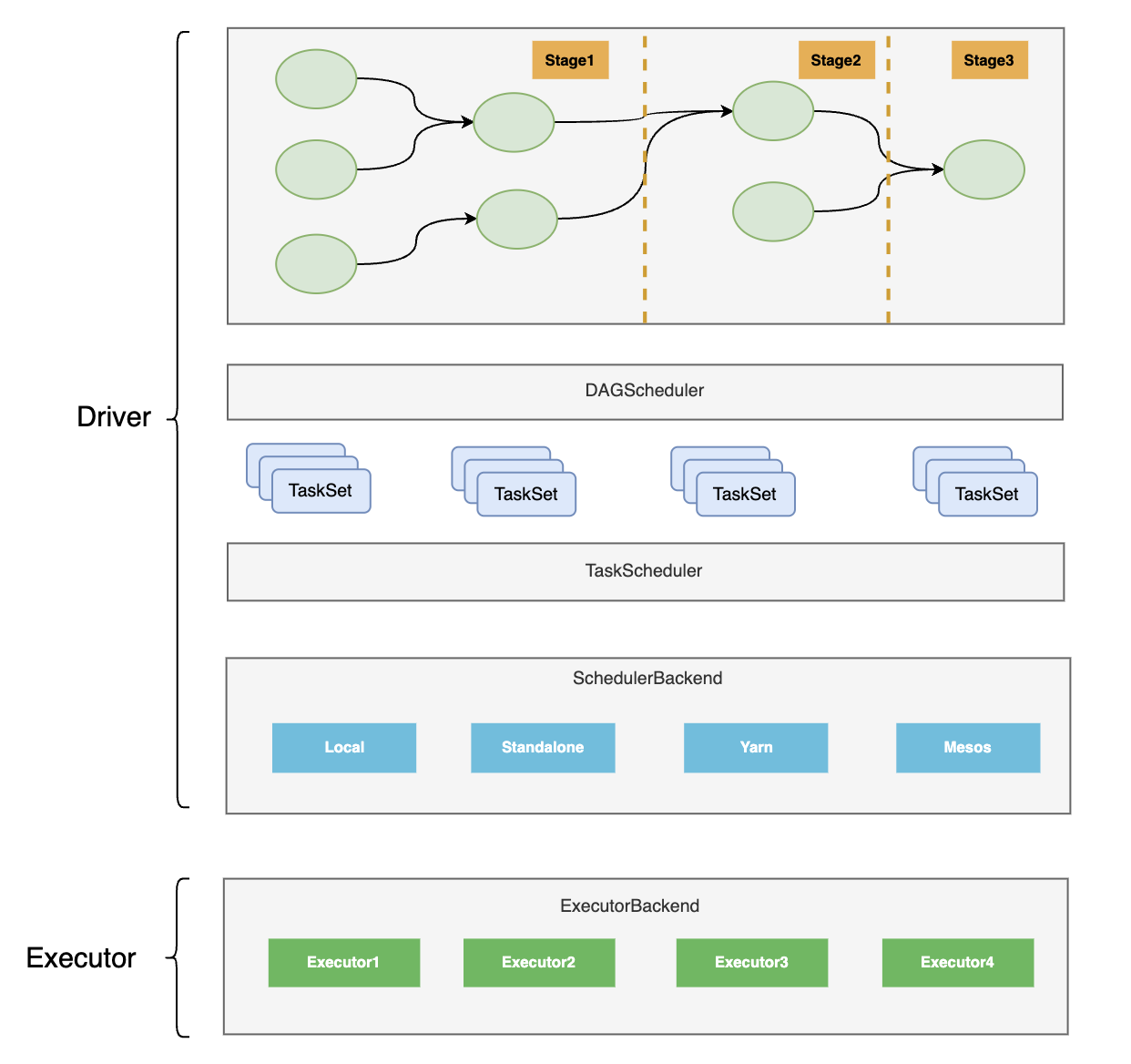
# 1. TaskScheduler 在调度中的位置
DAGScheduler 实际上是对 Stage 的调度,它将 Stage 中的 TaskSet 提交给 TaskScheduler。所以也可以说 DAGScheduler 是对 TaskSet 的调度。
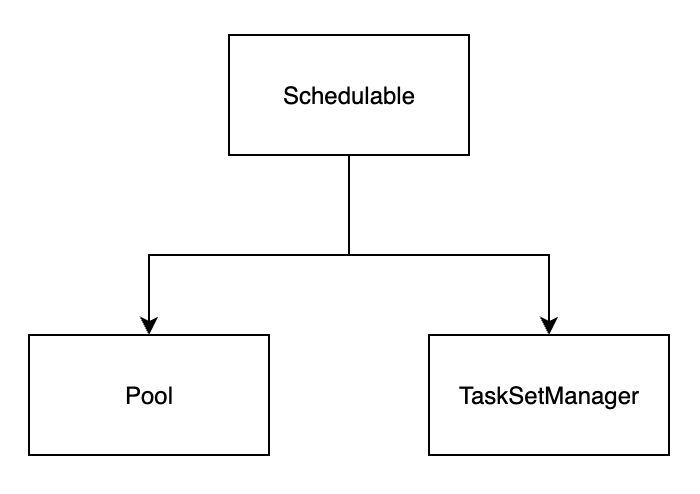
TaskScheduler 实现了对 Task 的调度,但是它直接调度的对象并不是 Task,而是 Schedulable(可调度实体的抽象),进而通过 Schedulable 的两个实现类 Pool 和 TaskSetManager 对 Task 进行调度(资源分配、状态跟踪、推断执行、本地性、失败重试等)。
TaskScheduler 是比 DAGScheduler 更 low level 的调度。
# 2. Schedulable 详解
Schedulable 是可调度实体的抽象,它有两个实现类:Pool 和 TaskSetManager。
Pool 中维护了可调度的子 Pool 以及 TaskSetManager 的集合。
TaskSetManager 针对在 TaskSchedulerImpl 单个 TaskSet 中的 task 进行调度,同时跟踪每个 task 状态。此类的主要接口是resourceOffer,它问询 TaskSet 是否要在一个节点上运行 task,以及根据 task 的运行结果(成功或失败)进行相应的处理。
Schedulable 源码如下:
private[spark] trait Schedulable {
// 父 Pool
var parent: Pool
// 可调度对象的列表,Schedulable 只有 Pool 和 TaskSetManager 两个子类
def schedulableQueue: ConcurrentLinkedQueue[Schedulable]
// 调度模式,可选值有 FAIR、FIFO、NONE
def schedulingMode: SchedulingMode
// 公平调度算法的权重
def weight: Int
// 公平调度算法的参考值
def minShare: Int
// 正在运行的 task 数量
def runningTasks: Int
// 调度的优先级
def priority: Int
// 所属 StageId
def stageId: Int
// PoolName
def name: String
// 添加 Schedulable
def addSchedulable(schedulable: Schedulable): Unit
// 删除 Schedulable
def removeSchedulable(schedulable: Schedulable): Unit
// 根据名称获取 Schedulable
def getSchedulableByName(name: String): Schedulable
// 某个 Executor 丢失后的处理
def executorLost(executorId: String, host: String, reason: ExecutorLossReason): Unit
// 检查当前 Pool 中是否有需要推断执行的任务
def checkSpeculatableTasks(minTimeToSpeculation: Int): Boolean
// 对于当前 Pool 中所有的 TaskSetManager 按照调度算法进行排序
def getSortedTaskSetQueue: ArrayBuffer[TaskSetManager]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
Pool 源码中有一个很重要的属性:
val schedulableQueue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue[Schedulable]
schedulableQueue 是一个 Schedulable 的队列,Schedulable 只有两个实现类 Pool 和 TaskSetManager。所以可以总结出调度池的抽象调度示意图:
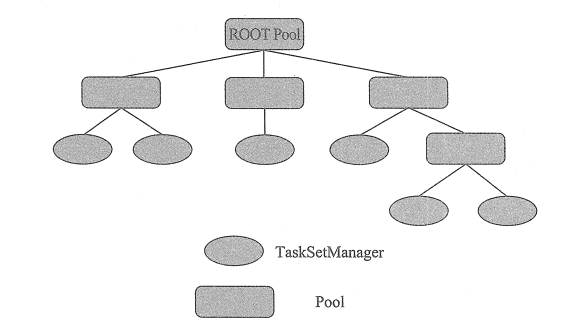
这仅仅只是抽象示意图,真正的实现根据调度算法的不同也不一样,如在 FIFO 调度算法中,调度池的抽象不是树状结构,而是一个队列(源码在 FIFOSchedulableBuilder 中):
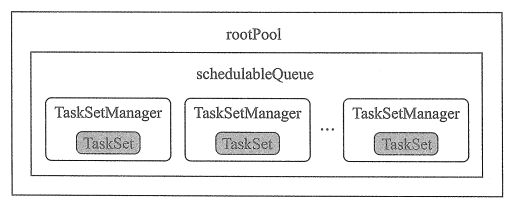
而当调度算法是 FAIR 时(源码在 FAIRSchedulableBuilder),调度池的抽象就和上面树状图很接近了。
# 2.1 Pool 源码
Pool 源码 实际上也比较简单。
private[spark] class Pool(
val poolName: String,
val schedulingMode: SchedulingMode, // 调度模式,可选值有 FAIR、FIFO、NONE
initMinShare: Int,
initWeight: Int)
extends Schedulable with Logging {
// 可调度对象的列表,Schedulable 只有 Pool 和 TaskSetManager 两个子类
val schedulableQueue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue[Schedulable]
val schedulableNameToSchedulable = new ConcurrentHashMap[String, Schedulable]
val weight = initWeight
val minShare = initMinShare
// 正在运行的 task 数
var runningTasks = 0
// 调度优先级
val priority = 0
// 所属 StageId
var stageId = -1
val name = poolName
// 父 Pool
var parent: Pool = null
// 确认调度算法,调度算法有公平调度和先进先出调度
// 对应的实现类分别是:FairSchedulingAlgorithm 和 FIFOSchedulingAlgorithm
private val taskSetSchedulingAlgorithm: SchedulingAlgorithm = {
schedulingMode match {
case SchedulingMode.FAIR =>
new FairSchedulingAlgorithm()
case SchedulingMode.FIFO =>
new FIFOSchedulingAlgorithm()
case _ =>
val msg = s"Unsupported scheduling mode: $schedulingMode. Use FAIR or FIFO instead."
throw new IllegalArgumentException(msg)
}
}
// 添加 Schedulable
override def addSchedulable(schedulable: Schedulable): Unit = {
require(schedulable != null)
schedulableQueue.add(schedulable)
schedulableNameToSchedulable.put(schedulable.name, schedulable)
schedulable.parent = this
}
// 移除 Schedulable
override def removeSchedulable(schedulable: Schedulable): Unit = {
schedulableQueue.remove(schedulable)
schedulableNameToSchedulable.remove(schedulable.name)
}
// 根据名称查找 Schedulable
override def getSchedulableByName(schedulableName: String): Schedulable = {
if (schedulableNameToSchedulable.containsKey(schedulableName)) {
return schedulableNameToSchedulable.get(schedulableName)
}
// 如果在当前 Pool 中没找到,则挨个从子 Schedulable 递归查找
for (schedulable <- schedulableQueue.asScala) {
val sched = schedulable.getSchedulableByName(schedulableName)
if (sched != null) {
return sched
}
}
null
}
// 当一个 Executor 丢失后,递归调用各个子 Schedulable 中的 executorLost 方法
// 实际上最终都执行的是 TaskSetManager executorLost 方法
override def executorLost(executorId: String, host: String, reason: ExecutorLossReason): Unit = {
schedulableQueue.asScala.foreach(_.executorLost(executorId, host, reason))
}
// 检查当前 Pool 中是否有需要推断执行的任务,递归调用各个子 Schedulable 的 checkSpeculatableTasks
// 实际上最终都执行的是 TaskSetManager checkSpeculatableTasks 方法
override def checkSpeculatableTasks(minTimeToSpeculation: Int): Boolean = {
var shouldRevive = false
for (schedulable <- schedulableQueue.asScala) {
shouldRevive |= schedulable.checkSpeculatableTasks(minTimeToSpeculation)
}
shouldRevive
}
// 对于当前 Pool 中所有的 TaskSetManager 按照调度算法进行排序
// 实际上最终都执行的是 TaskSetManager getSortedTaskSetQueue 方法
override def getSortedTaskSetQueue: ArrayBuffer[TaskSetManager] = {
val sortedTaskSetQueue = new ArrayBuffer[TaskSetManager]
val sortedSchedulableQueue =
schedulableQueue.asScala.toSeq.sortWith(taskSetSchedulingAlgorithm.comparator)
for (schedulable <- sortedSchedulableQueue) {
sortedTaskSetQueue ++= schedulable.getSortedTaskSetQueue
}
sortedTaskSetQueue
}
def increaseRunningTasks(taskNum: Int): Unit = {
runningTasks += taskNum
if (parent != null) {
parent.increaseRunningTasks(taskNum)
}
}
def decreaseRunningTasks(taskNum: Int): Unit = {
runningTasks -= taskNum
if (parent != null) {
parent.decreaseRunningTasks(taskNum)
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
# 2.2 TaskSetManager 源码
TaskSetManager,从名字就可以看出来是 TaskSet 的管理器,那么首先看看 TaskSet 是什么。
TaskSet 的源码如下,比较简单。它是一批 task 的集合,代表着某个 Stage 中一组 partition 的计算任务,这些 task 集合会被一起提交给 TaskScheduler。
private[spark] class TaskSet(
val tasks: Array[Task[_]], // Task 数组
val stageId: Int, // 所属的 StageId
val stageAttemptId: Int, // 所属的 Stage 尝试的 id
val priority: Int, // 优先级
val properties: Properties) {
val id: String = stageId + "." + stageAttemptId
override def toString: String = "TaskSet " + id
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
TaskSetManager 源码的内容比较多,先整体看一下它的属性,再看一些核心的方法。
private[spark] class TaskSetManager(
sched: TaskSchedulerImpl, // TaskSetManager 所属的 TaskSchedulerImpl
val taskSet: TaskSet, // 当前 TaskSetManager 管理的 TaskSet
val maxTaskFailures: Int, // Task 可允许的最大失败次数
blacklistTracker: Option[BlacklistTracker] = None,
clock: Clock = new SystemClock()) extends Schedulable with Logging {
// SparkConf
private val conf = sched.sc.conf
// Task 运行需要的 jar 和 file
private val addedJars = HashMap[String, Long](sched.sc.addedJars.toSeq: _*)
private val addedFiles = HashMap[String, Long](sched.sc.addedFiles.toSeq: _*)
// 结果的总字节大小限制
val maxResultSize = conf.get(config.MAX_RESULT_SIZE)
// SparkEnv
val env = SparkEnv.get
// 序列化器
val ser = env.closureSerializer.newInstance()
val tasks = taskSet.tasks
private[scheduler] val partitionToIndex = tasks.zipWithIndex.map { case (t, idx) => t.partitionId -> idx }.toMap
val numTasks = tasks.length
val copiesRunning = new Array[Int](numTasks)
// 是否启用任务的推测执行,默认不启用
val speculationEnabled = conf.get(SPECULATION_ENABLED)
// 机型推测前任务需要完成多少,默认0.75
val speculationQuantile = conf.get(SPECULATION_QUANTILE)
// 任务延迟的比例,比如当75%的task都完成,那么取他们的中位数跟还未执行完的任务作对比。如果超过1.5倍,则开启推测执行。
val speculationMultiplier = conf.get(SPECULATION_MULTIPLIER)
val minFinishedForSpeculation = math.max((speculationQuantile * numTasks).floor.toInt, 1)
val speculationTaskDurationThresOpt = conf.get(SPECULATION_TASK_DURATION_THRESHOLD)
val speculationTasksLessEqToSlots = numTasks <= Math.max(conf.get(EXECUTOR_CORES) / sched.CPUS_PER_TASK, 1)
// 记录每个 Task 是否执行成功的数组
val successful = new Array[Boolean](numTasks)
// 对每个 Task 执行失败次数机型记录的数组
private val numFailures = new Array[Int](numTasks)
// 当 Task 被其它 Task 尝试 kill 时,将被 kill 的 Task 记录到此
private val killedByOtherAttempt = new HashSet[Long]
// 对每个 Task 的执行失败次数进行记录的数组
val taskAttempts = Array.fill[List[TaskInfo]](numTasks)(Nil)
private[scheduler] var tasksSuccessful = 0
// 用于公平调度算法的权重
val weight = 1
// 用于公平调度算法的参考值
val minShare = 0
// 调度的优先级
var priority = taskSet.priority
// 调度池所属的 StageId
var stageId = taskSet.stageId
val name = "TaskSet_" + taskSet.id
var parent: Pool = null
// 所有 Task 执行总结果的大小
private var totalResultSize = 0L
// 计算过的 Task 数量
private var calculatedTasks = 0
// 正在运行的 Task 集合
private[scheduler] val runningTasksSet = new HashSet[Long]
override def runningTasks: Int = runningTasksSet.size
// 是否进入僵尸状态
private[scheduler] var isZombie = false
private[scheduler] def isBarrier = taskSet.tasks.nonEmpty && taskSet.tasks(0).isBarrier
// 存储按照本地性首选安排的处于等待状态的任务
private[scheduler] val pendingTasks = new PendingTasksByLocality()
// 可推测执行的 Task 集合
private[scheduler] val speculatableTasks = new HashSet[Int]
// 按本地性首选存储的可推测 Task 的集合
private[scheduler] val pendingSpeculatableTasks = new PendingTasksByLocality()
// Task 身份标识与 TaskInfo
private[scheduler] val taskInfos = new HashMap[Long, TaskInfo]
val successfulTaskDurations = new MedianHeap()
// 异常打印到日志的时间间隔
val EXCEPTION_PRINT_INTERVAL = conf.getLong("spark.logging.exceptionPrintInterval", 10000)
private val recentExceptions = HashMap[String, (Int, Long)]()
val epoch = sched.mapOutputTracker.getEpoch
// Task 本地性级别的数组
private[scheduler] var myLocalityLevels = computeValidLocalityLevels()
private[scheduler] var localityWaits = myLocalityLevels.map(getLocalityWait)
private var currentLocalityIndex = 0 // Index of our current locality level in validLocalityLevels
private var lastLaunchTime = clock.getTimeMillis() // Time we last launched a task at this level
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
# 3. SchedulerBackend 详解
# 3.1 SchedulerBackend 作用
在开始看 TaskScheduler 源码之前,需要先看看 SchedulerBackend,因为 TaskScheduler 的实现离不开它。
TaskScheduler 是在 SparkContext 中创建并初始化的,在 SparkContext 中调用 TaskSchedulerImpl(TaskScheduler 的唯一实现类)的初始化方法时需要传入 SchedulerBackend 作为参数。
SchedulerBackend 是 TaskScheduler 的调度后端接口。TaskScheduler 给 Task 分配资源实际是通过 SchedulerBackend 完成的,SchedulerBackend 给 Task 分配完资源后将与分配给 Task 的 Executor 通信,并要求 Executor 运行 Task。
注意
说实话,光看前面这些官话,我自己也看的很懵逼,还是没懂 SchedulerBackend 到底是干嘛的。
接着往下看~
注意前面说的加粗那句话“与分配给 Task 的 Executor 通信”,DAGScheduler 以及 TaskSchedule 都是在 Driver 段运行的,但是最终的 Task 却是在 Executor 运行的。Driver 需要为 Task 分配资源,还要了解 Task 的运行状态(LAUNCHING、RUNNING、FINISHED、FAILED、KILLED、LOST),所以 Driver 必须要和 Executor 进行 RPC 通信。SchedulerBackend 就是为了和 Executor 通信服务的,与 SchedulerBackend 对应的还有一个组件叫 ExecutorBackend。前者是在 Driver 端,后者是在 Executor 端。
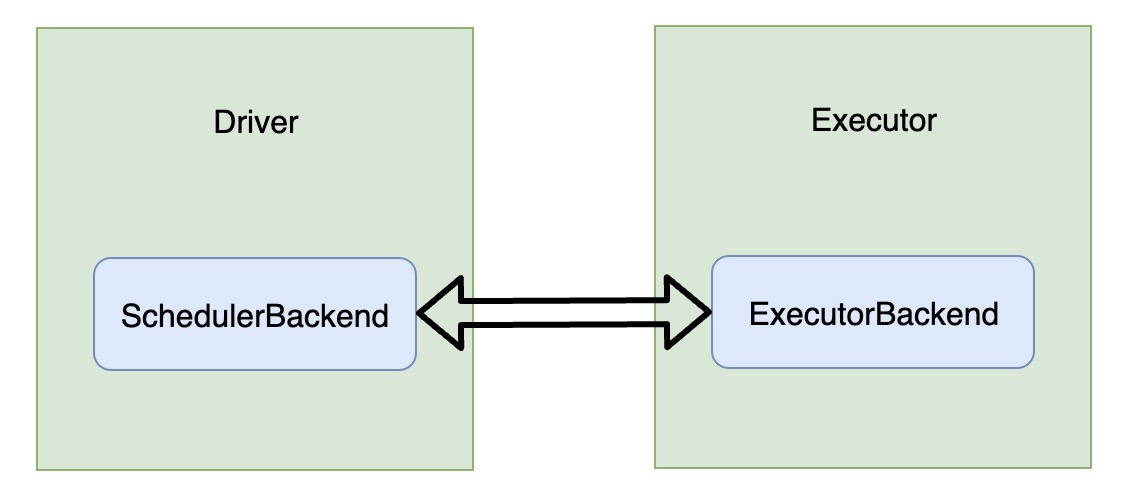
SchedulerBackend 和 ExecutorBackend 都是接口。前者的实现较为丰富,而 ExecutorBackend 的唯一实现类是 CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend,Executor 的真正线程就是在 CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend 中执行的。
# 3.2 SchedulerBackend 实现
SchedulerBackend 只是定义了一些接口,它的实现类如下:
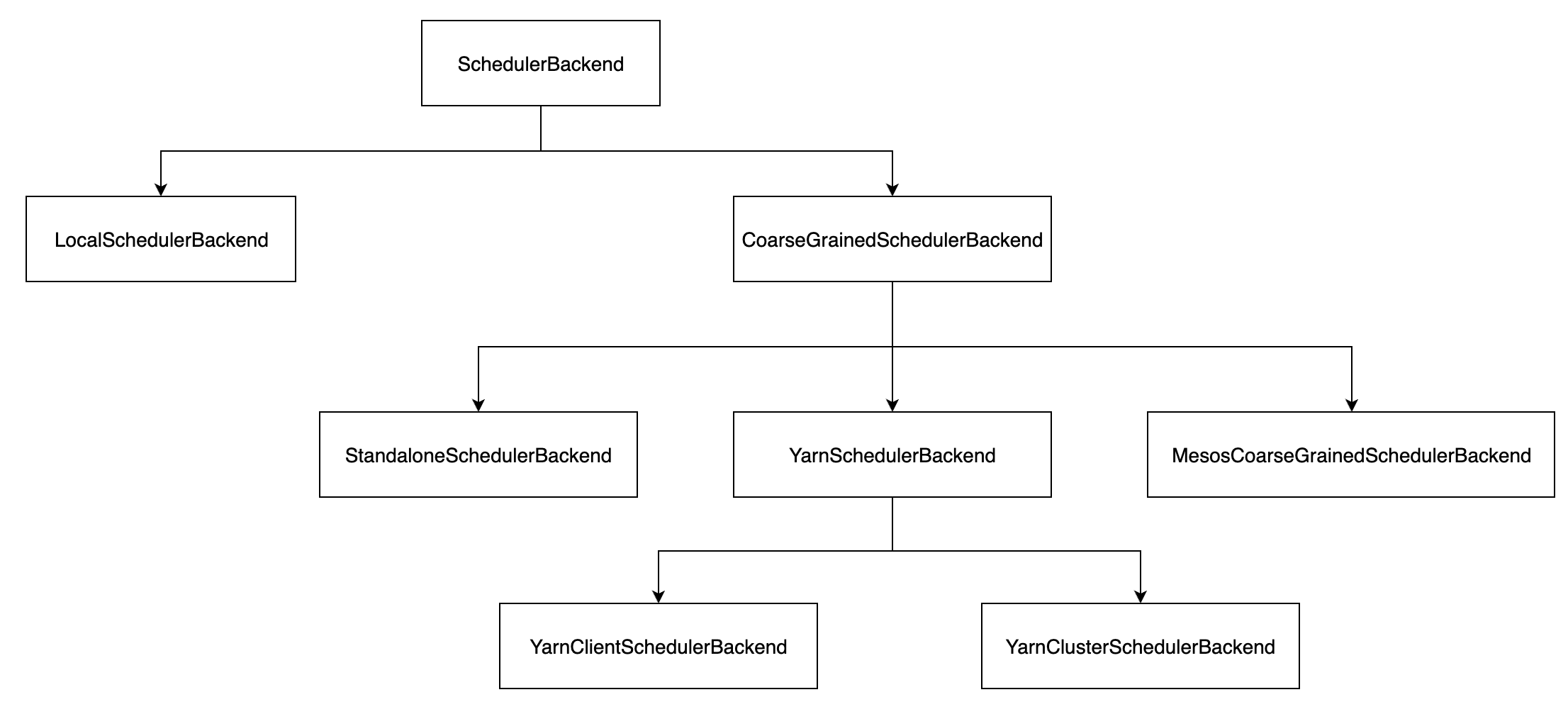
- LocalSchedulerBackend:local 模式中的调度后端接口。在 local 模式下,Driver、Executor、LocalSchedulerBackend 都运行在同一个 JVM 进程中。
- CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend:等待 CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend 进行连接的 SchedulerBackend 实现。由 CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend 建立的 CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend 进程将会一直存在,真正的 Executor 线程将在 CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend 进程中执行。
- StandaloneSchedulerBackend 是部署在 Standalone 模式下的 SchedulerBackend 实现。
- MesosCoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend:是部署在 Mesos 模式下的实现。
- YarnSchedulerBackend:是部署在 Yarn 模式下的实现,并且有 YarnClientSchedulerBackend 和 YarnClusterSchedulerBackend 两个子类。
SchedulerBackend 中定义了所有调度后端的接口:
private[spark] trait SchedulerBackend {
// 与当前 Job 相关联的应用程序的身份标识
private val appId = "spark-application-" + System.currentTimeMillis
// 启动 SchedulerBackend
def start(): Unit
// 停止 SchedulerBackend
def stop(): Unit
// 给调度池中的所有 Task 分配资源
def reviveOffers(): Unit
// 获取 Job 的默认并行度
def defaultParallelism(): Int
// 杀死指定 Task
def killTask(
taskId: Long,
executorId: String,
interruptThread: Boolean,
reason: String): Unit =
throw new UnsupportedOperationException
// SchedulerBackend 是否准备就绪
def isReady(): Boolean = true
// 获取 appId
def applicationId(): String = appId
// 当使用 cluster 模式运行并且集群管理器支持多次尝试时,此方法可以获取应用程序尝试的标识。
// 当应用程序在 client 模式运行时,将不支持多次尝试。
def applicationAttemptId(): Option[String] = None
// 获取 Driver 日志的 URL,这些 URL 会在 Spark UI 的 Executors 标签页中展示
def getDriverLogUrls: Option[Map[String, String]] = None
// 获取 Driver 的属性。当指定自定义日志 URL 模式时,这些属性用于替换日志 URL。
def getDriverAttributes: Option[Map[String, String]] = None
// 获取当前可并发启动的最大 Task 数
def maxNumConcurrentTasks(): Int
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
# 4. TaskScheduler 详解
TaskScheduler 是相对 DAGScheduler 更 low level 的调度器的规范,目前由 TaskSchedulerImpl 独家实现。每个 TaskScheduler 为单个 SparkContext 服务。TaskSchedule 从 DAGScheduler 获取提交给它们的 TaskSet,并负责将 Task 发送到集群运行、在出现故障时重试、并通过推断执行以及本地性等措施提高运行效率。