组合模式
# 一、概述
组合(Composite)模式,将对象组合成树状结构,并且能像使用独立对象一样使用它们。
组合模式的核心是被管理对象能够用树形结构来表示。
# 1.1 解决了什么问题
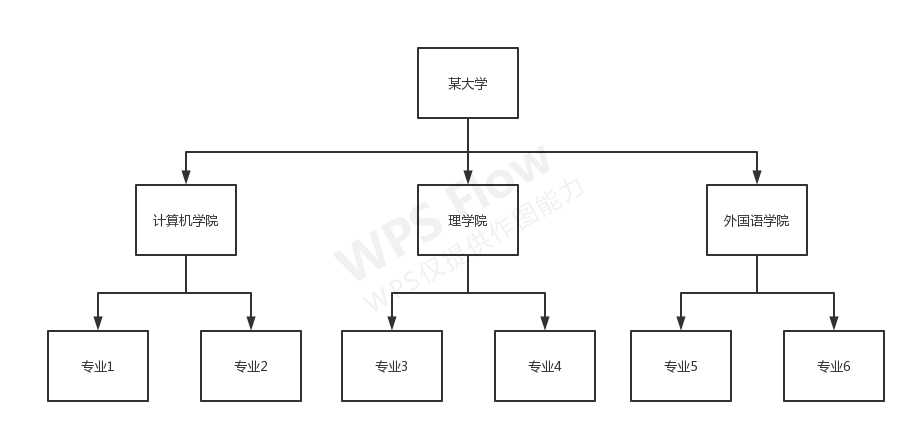
对于上图表示的这样一个树形结构,实际上是有是三个层级关系,如果要通过传统的方式对其进行管理,那么必须要定义三个类。对于每个类都要实现对应的增删改查操作。如果层级变得更深一点,专业下面加了班级,班级下班加了小组,意味着还要再增加新的类,而且对于每个新增的类都需要去实现对应的管理方法。
# 1.2 解决方案
对于树形结构而言,如果按照传统的方式每一层都定义为一个类的话是不现实的。在组合模式的思想里无需关系树形结构中的每一层具体是什么对象,而是将其看做成一个组合,对于任意一层的操作都以相同的方式进行处理,即无论操作哪一层,暴露给客户端的接口都是相同的。
# 二、实现方式
# 2.1 角色
- Component:用来描述树结构中所有对象的共有的接口。
- Leaf:树结构中的叶子结点。
- Composite:非叶子结点,无需关心自己的子结点,只需通过 Component 中的接口和子结点进行交互。
- Client:通过 Component 接口与所有结点进行交互。
# 2.2 代码
在 Component 中定义组合的共用操作接口:
public abstract class OrgComponent {
// 结点名称
public String name;
// 当前结点人数
public int userCount;
public List<OrgComponent> subOrgs = new ArrayList<>();
public OrgComponent(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public OrgComponent(String name, int userCount) {
this.name = name;
this.userCount = userCount;
}
/**
* 添加子结点
*
* @param org
* @throws Exception
*/
public abstract void addSubOrg(OrgComponent org) throws Exception;
/**
* 获取子结点个数
*
* @return
*/
public abstract int getSubOrgCount();
/**
* 获取所有子结点人数
*
* @return
*/
public abstract int getSubOrgUserCount();
/**
* 获取所有子结点以及当前节点人数
*
* @return
*/
public abstract int getUserCount();
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
定义组合类,实现 Component 的所有抽象方法:
public class OrgComposite extends OrgComponent {
public OrgComposite(String name) {
super(name);
}
public OrgComposite(String name, int userCount) {
super(name, userCount);
}
@Override
public void addSubOrg(OrgComponent org) {
subOrgs.add(org);
}
@Override
public int getSubOrgCount() {
int count = 0;
for (OrgComponent subOrg : subOrgs) {
count += subOrg.subOrgs.size() + 1;
}
return count;
}
@Override
public int getSubOrgUserCount() {
int count = 0;
for (OrgComponent subOrg : subOrgs) {
if (subOrg instanceof OrgLeaf) {
count += subOrg.getUserCount();
} else {
count += subOrg.getSubOrgUserCount();
}
}
return count;
}
@Override
public int getUserCount() {
return userCount + getSubOrgUserCount();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
定义叶子结点,同样实现 Component 中的抽象方法,但是由于叶子结点没有子结点,所以对于个别方法的处理方式和组合类不同:
public class OrgLeaf extends OrgComponent {
public OrgLeaf(String name, int userCount) {
super(name, userCount);
}
@Override
public void addSubOrg(OrgComponent org) throws Exception {
throw new Exception("叶子结点,无法停添加子结点");
}
@Override
public int getSubOrgCount() {
return subOrgs.size();
}
@Override
public int getSubOrgUserCount() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public int getUserCount() {
return userCount;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
客户端
public class CompositeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 每个学校结点和学院结点都有两个领导
OrgComponent root = new OrgComposite("XX大学", 2);
OrgComponent school1 = new OrgComposite("计算机学院", 2);
OrgComponent school2 = new OrgComposite("理学院", 2);
OrgComponent school3 = new OrgComposite("外国语学院", 2);
OrgComponent major1 = new OrgLeaf("专业1", 50);
OrgComponent major2 = new OrgLeaf("专业2", 30);
OrgComponent major3 = new OrgLeaf("专业3", 10);
OrgComponent major4 = new OrgLeaf("专业4", 20);
OrgComponent major5 = new OrgLeaf("专业5", 30);
OrgComponent major6 = new OrgLeaf("专业6", 40);
school1.addSubOrg(major1);
school1.addSubOrg(major2);
school2.addSubOrg(major3);
school2.addSubOrg(major4);
school3.addSubOrg(major5);
school3.addSubOrg(major6);
root.addSubOrg(school1);
root.addSubOrg(school2);
root.addSubOrg(school3);
System.out.println("学校总结点数:" + root.getSubOrgCount());
System.out.println("学校总人数:" + root.getUserCount());
System.out.println("学校子结点总人数:" + root.getSubOrgUserCount());
System.out.println("计算机学院子结点:" + school1.getSubOrgCount());
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
学校总结点数:9
学校总人数:182
学校子结点总人数:180
计算机学院子结点:2
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
# 三、源码中的应用
- java.util.Map#putAll(Map)
- java.util.List#addAll(Collection)
- java.util.Set#addAll(Collection)
上次更新: 2023/11/01, 03:11:44